Naval Architecture and Ship Building
Fore end structure: FWD Construction, Forward Construction
2 min read
0 comments
Engr. Shafiul Bari
Shafiul Bari is a seasoned Marine Engineer with extensive experience in ship design, maintenance, and marine propulsion systems. With a deep technical knowledge of ship engineering and a passion for advancing maritime technology, Shafiul shares practical insights and expert advice to help marine professionals and enthusiasts better understand the complexities of ship systems. Through his website, he aims to bridge the gap between technical theory and real-world application, fostering a community of informed and skilled maritime engineers.
When not immersed in ship engines and technical manuals, Shafiul enjoys exploring the latest innovations in marine technology and mentoring aspiring marine engineers.
View Author Profile →.FWD Construction .forward construction .fwdc .fore end construction
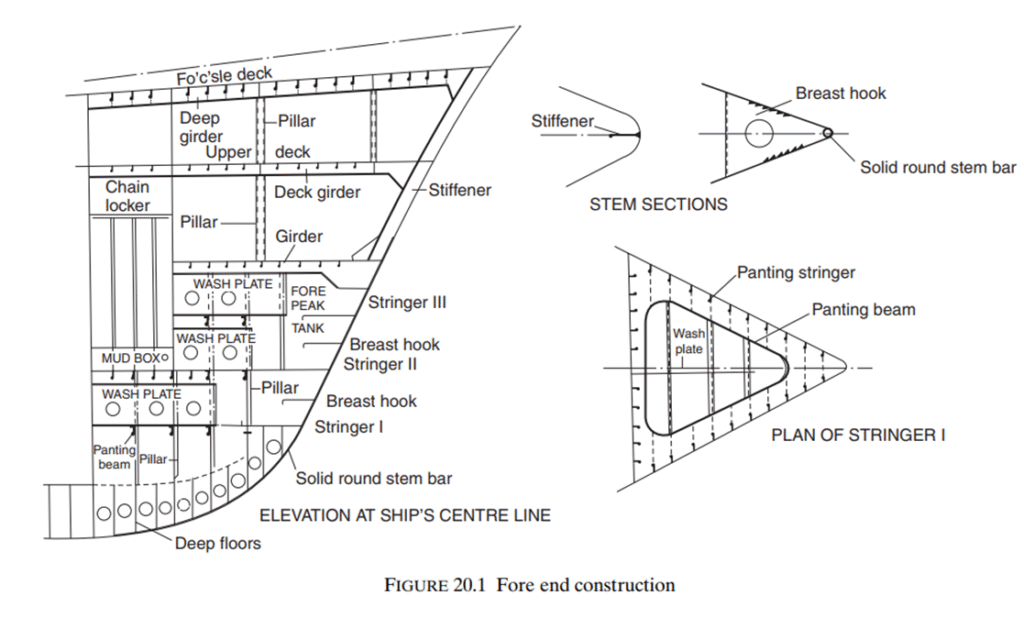
- FWD construction is forward of the collision bulkhead.
- The chain locker is included as it is usually fitted forward of the collision bulkhead below the second deck or upper deck, or in the forecastle itself
- On the forecastle deck the heavy windlass seating is securely fastened and given considerable support. The deck plating thickness is increased locally, and smaller pillars with heavier beams and a centre line pillar bulkhead, may be fitted below the windlass.
Stem
- On many conventional ships a stem bar, which is a solid round bar, is fitted from the keel to the waterline region, and a radiused plate is fitted above the waterline to form the upper part of the stem.
- This forms a ‘soft nose’ stem, which in the event of a collision will buckle under load, keeping the impact damage to a minimum.
- The solid round bar is welded inside the keel plate at its lower end, and inside the radiused stem plate at its upper end,
- the shell is welded each side to the radiused plate.
- breast hooks’ is used to support that part of the stem which is formed by radiused plates between the decks and below the lowest deck, to reduce the unsupported span of the stem.
- Panting stringer provided to counteract the panting stress. Panting stringer are triangular shape. Panting stringer are situated 2 meter above the keel and every 2 meter apart one panting stringer is fitted.
- Where the plate radius is large, further stiffening is provided by a vertical stiffener on the centre line.
- The thickness of these plates is greater than the forward side shell, but the thickness may taper near the side shell at the stem head.
Share this article
Leave a Comment
Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!